Delta Flight DL275 Japan Diversion to LAX – What Went Wrong?
Introduction
Long-haul international flights are usually the result of careful planning, built around multiple layers of safety and backup systems to ensure everything runs smoothly. Still, aviation operates in the real world, where unforeseen technical problems can arise despite the best preparation. That reality came into focus with Delta Flight DL275, a transpacific journey scheduled to carry passengers from Detroit to Tokyo that ultimately diverted to Los Angeles. The unexpected change quickly drew attention from travelers and aviation observers alike, sparking widespread discussion around the Delta flight DL275 Japan diversion LAX incident. Questions naturally followed: what prompted such a significant deviation from the original route, and what issue emerged? At the same time, the aircraft was airborne; how did the airline handle the situation once the aircraft safely reached the ground?
This article takes a close, ground-level look at what happened with Delta Flight DL275’s diversion to Los Angeles, walking through the events as they unfolded and explaining the reasons behind them in clear, practical terms. It examines the technical issue that led to the decision, how passengers experienced the disruption, and how the airline responded once the aircraft was on the ground. Taken together, the incident offers a valuable window into how modern aviation safety procedures work when plans change unexpectedly at 35,000 feet.
Flight Overview: Delta Flight DL275
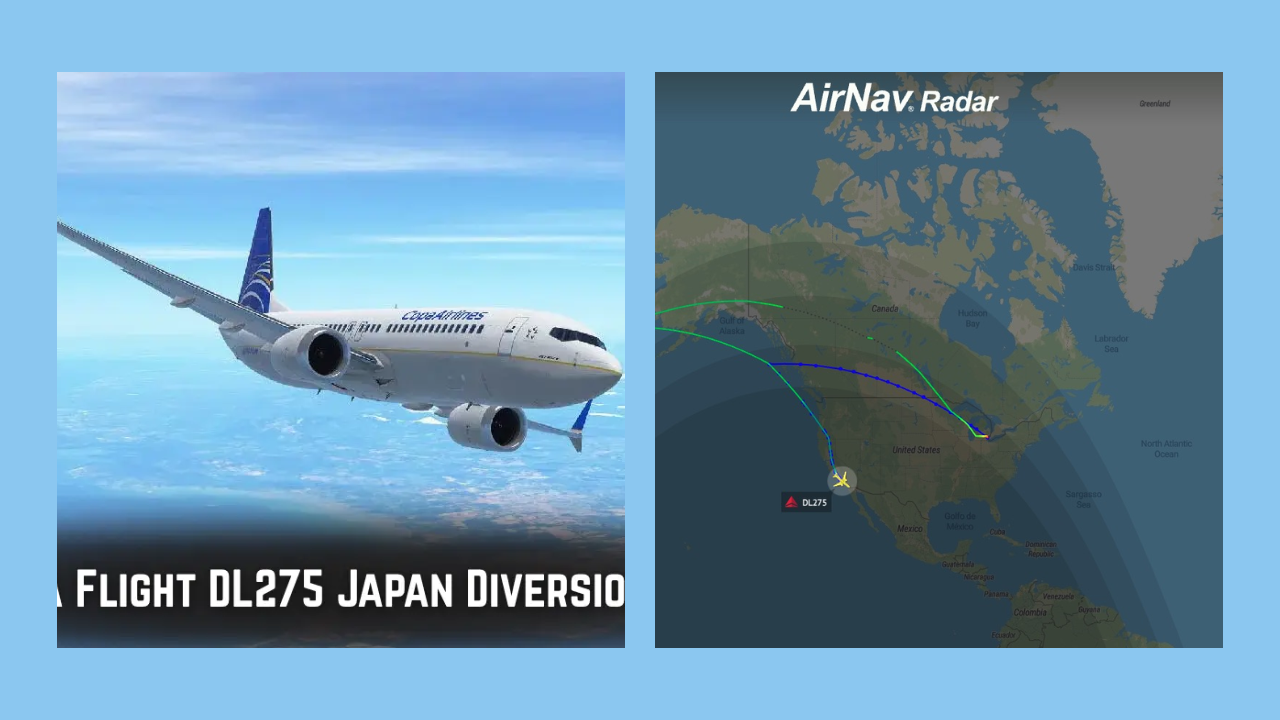
Delta Flight DL275 operates as one of Delta Air Lines’ regular long-distance international services, linking the U.S. Midwest with major destinations in East Asia. On the day of the diversion, the flight departed from Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport with a full complement of passengers and crew aboard an Airbus A350-900. This wide-body aircraft is a common choice for flights spanning oceans and continents, valued by airlines for its range, fuel efficiency, and advanced systems that enable reliable operation on some of the world’s longest nonstop routes.
The nonstop flight was scheduled to take roughly 12 to 13 hours, carrying passengers directly to Tokyo Haneda Airport. Those on board included business travelers, vacationers, and others connecting onward to destinations across Japan and the wider Asia-Pacific region. Nothing out of the ordinary was apparent at departure, and the aircraft left Detroit on time, settling into what initially seemed like a standard, uneventful crossing of the Pacific.
Planned Route and Destination
Flights operating between Detroit and Tokyo typically take a northerly path across the Pacific, arcing over Canada and stretching across the upper reaches of the ocean before turning south toward Japan. This route isn’t chosen at random—it balances fuel efficiency with practical safety considerations, ensuring the aircraft remains within reach of suitable alternate airports while also keeping overall flight time and fuel consumption in check.
Delta Flight DL275 was scheduled to land at Tokyo’s Haneda Airport, one of the country’s busiest and most important aviation hubs, serving the capital and its surrounding region. For passengers on board, the expectation was a straightforward nonstop arrival in Japan, with no disruptions en route. That assumption held for the first part of the journey, but as the flight progressed, circumstances emerged that ultimately sent the aircraft in a completely different direction.
What Happened Mid‑Flight?
About five hours into the flight, as the aircraft cruised at its normal altitude over the Pacific, the cockpit received indications that something wasn’t operating as expected. Flight data and subsequent reporting indicated an issue with the aircraft’s engine anti-ice system, a key component designed to protect engines in cold, high-altitude environments. At those elevations, ice can form rapidly under certain conditions, making systems such as anti-ice protection essential for maintaining normal engine performance and overall flight safety.
The engine anti-ice system prevents ice formation by directing hot air to areas of the engine where ice is most likely to form. Without that protection, ice can accumulate and disrupt the smooth flow of air through the engine, thereby affecting its performance. When a system like this isn’t functioning as intended, flight crews are trained to take a cautious approach—particularly on long stretches over open water, where alternate airports may be few and far between.
Although the aircraft was flying normally and passengers were never in immediate danger, the system warning could not be ignored. Continuing toward Japan would have meant several more hours at sea with an unresolved technical issue. Instead, the pilots began working with Delta’s operations team on the ground to assess the situation and identify the safest and most practical airport where the flight could land if a diversion became necessary.
Why the Diversion Decision Was Made
Although everything about the flight appeared stable from a passenger’s perspective, the warning in the cockpit was severe enough that it couldn’t be dismissed. Pushing on toward Japan would have kept the aircraft over vast stretches of open ocean for hours while a technical question remained unanswered. Faced with that reality, the flight crew shifted focus to contingency planning, coordinating closely with Delta’s ground operations team to evaluate their options and determine the most appropriate and safest place to land the aircraft if a diversion became the best course of action.
By that point in the flight, returning to Detroit was no longer a realistic option, as the aircraft had already covered a significant portion of the journey. The crew instead focused on finding an airport that could handle a wide-body jet without difficulty, had the technical resources to address a complex maintenance issue, and could support hundreds of displaced passengers. After weighing those factors, Los Angeles International Airport emerged as the most practical choice, leading to the decision to divert the flight there.
Once the decision was made, the diversion unfolded smoothly and without incident. The flight changed course, followed standard descent procedures, and landed at Los Angeles International Airport without complications. No injuries were reported, and nothing about the landing itself suggested an emergency, underscoring that the move to LAX was a precautionary measure rather than a response to an immediate threat.
Why Los Angeles Was Chosen as the Diversion Airport
At first, diverting a Midwest-to-Japan flight to Los Angeles might seem counterintuitive. Distance alone, however, is rarely the deciding factor when crews plan an unscheduled landing. In this case, Los Angeles International Airport checked several critical boxes that outweighed simple geography, making it a logical and well-supported choice for Delta Flight DL275 once a diversion became necessary.
One of the most significant advantages of diverting to LAX is the depth of its maintenance and technical capabilities. As a central international hub, the airport is fully equipped to support complex wide-body aircraft such as the Airbus A350. Issues involving engine systems cannot be addressed anywhere—they require specialized tools, experienced engineers, and certified technicians, all of which are readily available at an airport of LAX’s scale.
Another key factor was the airport’s physical layout and capabilities. Los Angeles has multiple long runways designed to handle heavy, long-haul aircraft arriving with substantial fuel loads. In addition to runway length, the airport offers extensive ground handling resources tailored to wide-body jets, from specialized equipment to experienced ramp crews. Together, these features enable an aircraft to land without restrictions and proceed quickly into maintenance and servicing upon arrival at the gate.
From the passenger side of the equation, Los Angeles also makes practical sense. As a central global hub, LAX is accustomed to handling large-scale disruptions and the sudden arrival of hundreds of unexpected travelers. The availability of nearby hotels, a wide range of alternative flight options, and on-site customer service staff give the airline greater flexibility to assist passengers, rebook itineraries, and provide accommodations than a smaller or less connected airport could offer.
Passenger Experience During the Diversion
For those on board Delta Flight DL275, the change in plans was sudden and largely unexpected. As the aircraft altered course, flight attendants and the cockpit crew kept passengers informed, explaining that a technical concern made a stop in Los Angeles the safest option. While news of a diversion can understandably make travelers uneasy, the calm tone of the announcements and the steady flow of information helped reassure many that the situation was being handled carefully and professionally.
As the plane made its approach into Los Angeles, there was nothing out of the ordinary for those in the cabin. The landing was routine, followed by a regular taxi to the gate, with no signs of urgency or distress. Upon arrival, passengers received clear instructions on the next steps, including how to exit the aircraft and where to obtain assistance with rebooking, accommodations, and other travel arrangements.
While the diversion inevitably led to delays and disrupted travel plans, many passengers later reflected that the steady communication and smooth landing helped put things into perspective. Knowing what was happening and seeing the situation handled calmly went a long way toward reducing frustration. Ultimately, the experience underscored a simple reality of air travel: diversions are inconvenient, but they exist for a reason, forming one of the many layers designed to keep passengers safe.
Delta Air Lines’ Response and Ground Operations
Once the aircraft was parked at the gate in Los Angeles, Delta Air Lines shifted into its established playbook for handling disrupted flights. Passengers were directed to airline staff who assisted with hotel arrangements, meal options, and rebooking onto later flights to Tokyo or alternative destinations. Behind the scenes, airline representatives worked to coordinate connections and minimize further delays, aiming to help travelers get back on track with minimal additional disruption.
While passengers were being attended to, the aircraft remained on the ground for a closer inspection. Maintenance crews began a comprehensive inspection of the engine anti-ice system, working methodically to pinpoint what triggered the warning in flight. That process typically involves a combination of hands-on mechanical checks and detailed system diagnostics, and it continues until engineers are delighted that the issue has been identified and resolved before the aircraft is cleared to fly again.
Overall, the situation was handled in accordance with well-established aviation norms that prioritize safety and passenger care. Although the diversion created complex logistical hurdles, the airline’s actions reflected a clear focus on managing the disruption responsibly, while ensuring that operational integrity and traveler well-being remained the top priorities.
Understanding the Engine Anti‑Ice System
The engine anti-ice system is an essential safeguard during high-altitude flight, where temperatures routinely drop far below freezing. Under those conditions, ice crystals can form rapidly and adhere to critical engine components. If that ice isn’t properly managed, it can interfere with airflow and compromise engine performance, making reliable anti-ice protection a key component of maintaining safe and stable operations in the air.
Modern aircraft are constantly monitoring themselves through automated systems that track the performance of critical components in real time. When the anti-ice system deviates from regular operation, cockpit alerts are displayed to draw the crew’s attention. Pilots are then guided by established checklists that outline the safest next steps, which may involve avoiding certain atmospheric conditions or choosing to land at an airport where the issue can be examined and resolved without unnecessary risk.
For Delta Flight DL275, the warning regarding the anti-ice system was taken seriously, even though the aircraft continued to operate normally. With many hours still ahead over remote stretches of the Pacific, the crew opted for the cautious approach. That decision reflected an understanding that addressing the issue sooner, rather than proceeding into more isolated airspace, was the most responsible course under the circumstances.
How Common Are International Flight Diversions?
Although international flight diversions tend to attract attention when they happen, they are a regular part of airline operations. With thousands of long-haul flights in the air every day, it’s inevitable that some will need to change course because of weather shifts, medical emergencies, technical concerns, or unexpected airspace restrictions. Most of these decisions are made quietly and routinely, guided by safety protocols rather than public visibility.
What distinguished the Delta Flight DL275 diversion was not only that it occurred but also where the aircraft ultimately landed. Choosing a central hub like Los Angeles over a closer alternate airport reflected a broader calculation that went beyond mileage alone. The decision illustrates how airlines simultaneously weigh several competing priorities—having adequate maintenance resources available, ensuring passengers are properly accommodated, and minimizing longer-term operational disruption—when making critical decisions in the air.
Tech Ultimate
Conclusion
The Delta flight DL275 Japan diversion LAX incident offers a clear look at how today’s aviation system responds when something doesn’t go according to plan. Although the aircraft did not reach its intended destination, the outcome reflected sound judgment by the flight crew, well-defined safety procedures, and seamless coordination with ground teams. Rather than signaling failure, the diversion demonstrated how built-in safeguards are designed to operate when circumstances change unexpectedly.
For those on the flight, the diversion was unwelcome but ended without harm. From the airline’s perspective, it served as a reminder of the necessity of caution when onboard systems don’t behave as expected. More broadly, the situation echoed a core principle of aviation: no schedule or destination matters more than protecting the people on board, even if that means changing plans mid-journey.
Ultimately, the decision to divert Delta Flight DL275 to Los Angeles wasn’t a breakdown in the system, but evidence that it was functioning as intended. The outcome reflected the application of established safety standards thoughtfully and effectively, ensuring that caution prevailed over convenience when it mattered most.






